Scroll Bars
With many VB controls, such as the listbox, multi-line textbox, treeview, listview, flex grid, and so on, vertical and/or horizontal scroll bars automatically appear on these controls and function as needed with little or no extra programming required. However, there may be times when you need to apply your own scroll bar functionality to an application. For such occasions, the Veritcal Scroll Bar and Horizontal Scroll Bar controls are available in the VB toolbox.
A scroll bar control consists of a bar with arrows at each end. Between the arrows is a square scroll box (also called a "thumb"). The scroll box slides along the scroll shaft between the two arrows.
Scroll bars are most frequently used to let the user move the contents of an area to bring into view a portion temporarily outside the visible region. A scroll bar control can also be used to specify a value within a prescribed range. By moving the scroll box between the two arrows, the user can specify a value in an intuitive, visual manner.
The scroll box on the scroll shaft indicates the current value specified by the bar. When the user clicks the arrow at either end of the scroll bar, the scroll box moves and incremental unit toward that arrow. When the user clicks the scroll shaft somewhere between an arrow and the scroll box, it moves a larger incremental unit toward the click position. In addition, the user can directly drag the scroll box along the shaft with the mouse.
When using a scroll bar control, you must determine the range of values that the control can designate. A scroll bar control can represent integer values in the range -32768 through +32767. You use the Min property to specify the low end of your range and the Max property to specify the high end of your range. The Value property specifies the current value represented by the scroll bar. The position of the scroll box along the scroll shaft graphically reflects where Value lies between Min and Max. If the user moves the scroll box, the Value property adjusts appropriately. If you modify the Vaue in program code, VB moves the scroll box to the appropriate position. The SmallChange property indicates how much the Value changes when the user clicks one of the arrows at the end of the scroll bar. The LargeChange indicates how much Value changes when the user clicks the scroll shaft between the scroll box and one of the arrows.
A Very Simple Example
In the very simple example that follows, a label is used to display the value of the scroll bar as it changes by the user clicking the arrows or moving the scroll box. To build the example, start a new project, place a label control and a vertical scroll bar (VScrollBar) control on the form and set their properties as indicated in the callouts below:
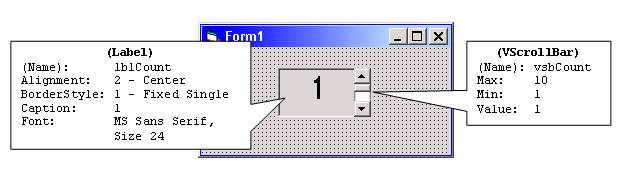
This sample program requires only a single line of code in the vertical scroll bar's Change event:
Private Sub vsbCount_Change()
lblCount.Caption = vsbCount.Value
End Sub
When you run the program, you will see that the value displayed in the label will vary as you click on the scroll bar's arrows or move its scroll box.
Note: When a scroll bar has focus, its scroll box will blink. Some people find this annoying. In most cases, you can prevent this blinking by setting the TabStop property of the scroll bar to False (the default is True). An exception to this is when the scroll bar is the only control on the form that can receive focus – such is the case in this example.
Download the VB project code for the example above here.
A More Advanced Example
In this example, a "manual" data grid has been created. With the various advanced controls that can be used with VB, such as the MS-FlexGrid, ListView, third-party girds, etc., you would most likely not have the need to build something like this – but you never know. This is a "low-tech" grid built with basic toolbox controls: a handful of labels, some images, a vertical scroll bar, and a horizontal scroll bar.
The application displays data about the twelve zodiac signs (Aires, Taurus, Gemini, Cancer, Leo, Virgo, Libra, Scorpio, Sagittarius, Capricorn, Aquarius, and Pisces). Note that there are only seven "rows" on the form, so vertical scrolling is necessary to view the twelve zodiac "records".
Associated with each sign are 15 fields: sign description, house, gemstone, New Age stone, colors, opposite sign, least compatible signs, ruling planet, element, anatomy, flower, most compatible signs, Tarot card, positive characteristics, and negative characteristics. Note that there are only four "columns" on the form, so horizontal scrolling is necessary to view the 15 fields.
When the program first runs, the form looks like this:
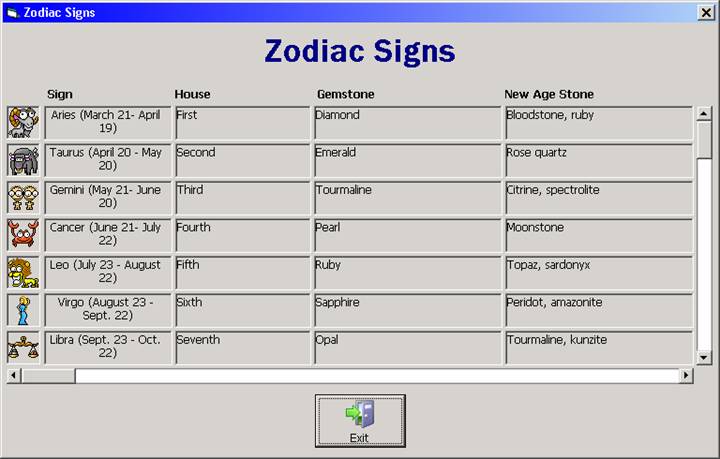
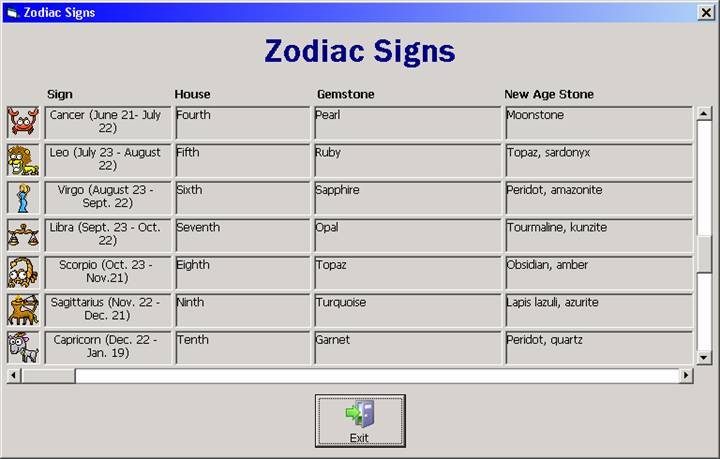
Screen shot after scrolling down (vertically):
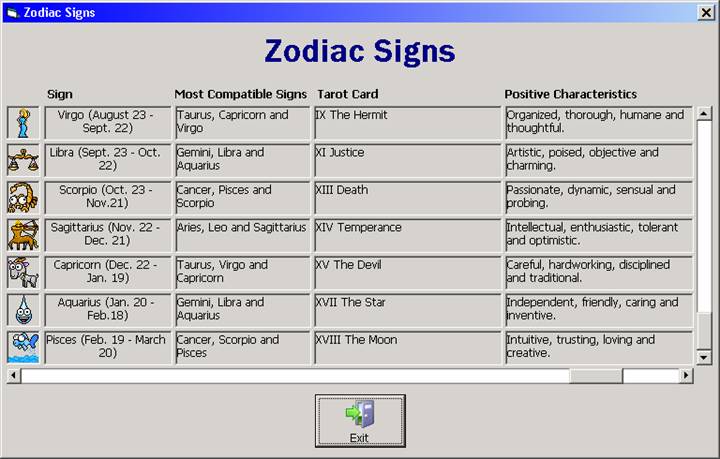
Screen shot after scrolling across (horizontally):
Building the Zodiac Example
To build the Zodiac example, place the controls on the form and set their properties as shown below:
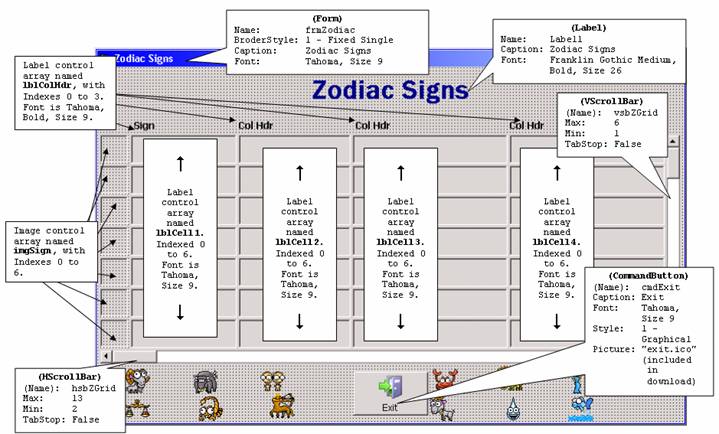
The Zodiac images at the bottom of the form serve as the image repository for the images displayed to the left of each sign row (in the imgSign array). These images form a control array named imgSourceSign, indexed 0 to 11. The Visible property for these images should be set to False. These images are .ico files and are included in the download. They were obtained from this website: http://virtualgraphicsworld.freeservers.com/zodiac.htm. The Picture property for the imgSourceSign array images should be set as follows:
|
Index |
Picture |
|
0 |
aires.ico |
|
1 |
taurus.ico |
|
2 |
gemini.ico |
|
3 |
cancer.ico |
|
4 |
leo.ico |
|
5 |
virgo.ico |
|
6 |
libra.ico |
|
7 |
scorpio.ico |
|
8 |
sagittarius.ico |
|
9 |
capricorn.ico |
|
10 |
aquarius.ico |
|
11 |
pisces.ico |
The program reads in a comma-delimited text file named "NewZodiac.txt". The data for the file is based on the information found on the following website: http://www.extonbiz.com/yoursign.html.
General Declarations Section
The General Declarations section declares a Type record structure based on the data in the input file. A UDT array variable is then defined as that Type. It is expected that exactly 12 records will be read from the input file, so the array is declared with a fixed number (12) of elements. Two form-level variables (mintRowStart and mintColStart) are also declared. These variables specify the row and column starting points for transferring data from the UDT array to the control arrays on the form.
Option Explicit
Private Type ZodiacRecord
SignDesc As String
House As String
Gemstone As String
NewAgeStone As String
Colors As String
OppositeSign As String
LeastCompat As String
RulingPlanet As String
Element As String
Anatomy As String
Flower As String
MostCompat As String
TarotCard As String
PositiveChars As String
NegativeChars As String
End Type
Private maudtZodiacRec(1 To 12) As ZodiacRecord
Private mintRowStart As Integer
Private mintColStart As Integer
Form_Load Event
The Form_Load event opens the "NewZodiac.txt" input file and loads it into the UDT record array. As the file is being read in, if the record count exceeds 12, an error message will be displayed and the program will end. Similarly, after the file has been read in, if there were fewer than 12 records loaded, an error message will be displayed and the program will end. The mintRowStart and mintColStart variables are initialized to 1 and 2 respectively. The SetColumnHeaders and DisplayZodiacData Subs are then called to provide the initial display of the data.
'----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Private Sub Form_Load()
'----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Dim intZFileNbr As Integer
Dim strFileName As String
Dim intSignX As Integer
intZFileNbr = FreeFile
strFileName = App.Path & IIf(Right$(App.Path, 1) = "\", "", "\") _
& "NewZodiac.txt"
Open strFileName For Input As #intZFileNbr
intSignX = 0
Do Until EOF(intZFileNbr)
intSignX = intSignX + 1
If intSignX > 12 Then
MsgBox "More than 12 zodiac records are present in the input file. " _
& "Please check the data and try again.", _
vbCritical, _
"Too Many Records"
End
End If
With maudtZodiacRec(intSignX)
Input #intZFileNbr, _
.SignDesc, _
.House, _
.Gemstone, _
.NewAgeStone, _
.Colors, _
.OppositeSign, _
.LeastCompat, _
.RulingPlanet, _
.Element, _
.Anatomy, _
.Flower, _
.MostCompat, _
.TarotCard, _
.PositiveChars, _
.NegativeChars
End With
Loop
Close #intZFileNbr
If intSignX < 12 Then
MsgBox "Fewer than 12 zodiac records are present in the input file. " _
& "Please check the data and try again.", _
vbCritical, _
"Too Few Records"
End
End If
mintRowStart = 1
mintColStart = 2
SetColumnHeaders
DisplayZodiacData
End Sub
hsbZGrid_Change Event
This event will occur when the user changes the value of the horizontal scroll bar by clicking on its arrows or dragging its scroll box. The value will be set to a number between 2 and 13, and this is assigned to mintColStart. The SetColumnHeaders and DisplayZodiacData Subs are then called to update the display based on the new value of the horizontal scroll bar.
'----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Private Sub hsbZGrid_Change()
'----------------------------------------------------------------------------
mintColStart = hsbZGrid.Value
SetColumnHeaders
DisplayZodiacData
End Sub
vsbZGrid_Change Event
This event will occur when the user changes the value of the vertical scroll bar by clicking on its arrows or dragging its scroll box. The value will be set to a number between 1 and 6, and this is assigned to mintRowStart. The DisplayZodiacData Sub is then called to update the display based on the new value of the vertical scroll bar.
'----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Private Sub vsbZGrid_Change()
'----------------------------------------------------------------------------
mintRowStart = vsbZGrid.Value
DisplayZodiacData
End Sub
cmdExit_Click Event
Ends the program.
'----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Private Sub cmdExit_Click()
'----------------------------------------------------------------------------
End
End Sub
SetColumnHeaders Sub
This Sub sets the column headings based on the current value of mintColStart (which will be a number from 2 to 13, the min/max range of the horizontal scroll bar). A set of headings from "House" thru "New Age Stone" (fields 2 thru 4) to "Tarot Card" thru "Negative Characteristics" (fields 13 thru 15) will be assigned to elements 1 thru 3 of the lblColHdr control array. Note that only elements 1, 2, and 3 of the lblColHdr control array are changed. Element 0 is reserved for "Sign", which remains frozen as the other columns scroll to the right or left.
'----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Private Sub SetColumnHeaders()
'----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Select Case mintColStart
Case 2
lblColHdr(1).Caption = "House"
lblColHdr(2).Caption = "Gemstone"
lblColHdr(3).Caption = "New Age Stone"
Case 3
lblColHdr(1).Caption = "Gemstone"
lblColHdr(2).Caption = "New Age Stone"
lblColHdr(3).Caption = "Colors"
Case 4
lblColHdr(1).Caption = "New Age Stone"
lblColHdr(2).Caption = "Colors"
lblColHdr(3).Caption = "Opposite Sign"
Case 5
lblColHdr(1).Caption = "Colors"
lblColHdr(2).Caption = "Opposite Sign"
lblColHdr(3).Caption = "Least Compatible Signs"
Case 6
lblColHdr(1).Caption = "Opposite Sign"
lblColHdr(2).Caption = "Least Compatible Signs"
lblColHdr(3).Caption = "Ruling Planet"
Case 7
lblColHdr(1).Caption = "Least Compatible Signs"
lblColHdr(2).Caption = "Ruling Planet"
lblColHdr(3).Caption = "Element"
Case 8
lblColHdr(1).Caption = "Ruling Planet"
lblColHdr(2).Caption = "Element"
lblColHdr(3).Caption = "Anatomy"
Case 9
lblColHdr(1).Caption = "Element"
lblColHdr(2).Caption = "Anatomy"
lblColHdr(3).Caption = "Flower"
Case 10
lblColHdr(1).Caption = "Anatomy"
lblColHdr(2).Caption = "Flower"
lblColHdr(3).Caption = "Most Compatible Signs"
Case 11
lblColHdr(1).Caption = "Flower"
lblColHdr(2).Caption = "Most Compatible Signs"
lblColHdr(3).Caption = "Tarot Card"
Case 12
lblColHdr(1).Caption = "Most Compatible Signs"
lblColHdr(2).Caption = "Tarot Card"
lblColHdr(3).Caption = "Positive Characteristics"
Case 13
lblColHdr(1).Caption = "Tarot Card"
lblColHdr(2).Caption = "Positive Characteristics"
lblColHdr(3).Caption = "Negative Characteristics"
End Select
End Sub
DisplayZodiacData Sub
This Sub populates the lblCell1, lblCell2, lblCell3, and lblCell4 control arrays based on the current values of mintRowStart and mintColStart. The mintRowStart variable will contain a value between 1 and 6, the min/max range of the vertical scroll bar. This means that data for records 1 thru 7, 2 thru 8, 3 thru 9, 4 thru 10, 5 thru 11, or 6 thru 12 will be loaded into elements 0 thru 6 of the lblCellx arrays. Similarly, the value of mintColStart will be a number from 2 to 13, the min/max range of the horizontal scroll bar. This means that the set of fields from "House" thru "NewAgeStone" (fields 2 thru 4) to "TarotCard" thru "NegativeChars" (fields 13 thru 15) will be loaded into the appropriate element of lblCell2, lblCell3, and lblCell4.
'----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Private Sub DisplayZodiacData()
'----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Dim intX As Integer
Dim intRecordIndex As Integer
intRecordIndex = mintRowStart
For intX = 0 To 6
With maudtZodiacRec(intRecordIndex)
lblCell1(intX).Caption = .SignDesc
imgSign(intX).Picture = imgSourceSign(intRecordIndex - 1).Picture
Select Case mintColStart
Case 2
lblCell2(intX).Caption = .House
lblCell3(intX).Caption = .Gemstone
lblCell4(intX).Caption = .NewAgeStone
Case 3
lblCell2(intX).Caption = .Gemstone
lblCell3(intX).Caption = .NewAgeStone
lblCell4(intX).Caption = .Colors
Case 4
lblCell2(intX).Caption = .NewAgeStone
lblCell3(intX).Caption = .Colors
lblCell4(intX).Caption = .OppositeSign
Case 5
lblCell2(intX).Caption = .Colors
lblCell3(intX).Caption = .OppositeSign
lblCell4(intX).Caption = .LeastCompat
Case 6
lblCell2(intX).Caption = .OppositeSign
lblCell3(intX).Caption = .LeastCompat
lblCell4(intX).Caption = .RulingPlanet
Case 7
lblCell2(intX).Caption = .LeastCompat
lblCell3(intX).Caption = .RulingPlanet
lblCell4(intX).Caption = .Element
Case 8
lblCell2(intX).Caption = .RulingPlanet
lblCell3(intX).Caption = .Element
lblCell4(intX).Caption = .Anatomy
Case 9
lblCell2(intX).Caption = .Element
lblCell3(intX).Caption = .Anatomy
lblCell4(intX).Caption = .Flower
Case 10
lblCell2(intX).Caption = .Anatomy
lblCell3(intX).Caption = .Flower
lblCell4(intX).Caption = .MostCompat
Case 11
lblCell2(intX).Caption = .Flower
lblCell3(intX).Caption = .MostCompat
lblCell4(intX).Caption = .TarotCard
Case 12
lblCell2(intX).Caption = .MostCompat
lblCell3(intX).Caption = .TarotCard
lblCell4(intX).Caption = .PositiveChars
Case 13
lblCell2(intX).Caption = .TarotCard
lblCell3(intX).Caption = .PositiveChars
lblCell4(intX).Caption = .NegativeChars
End Select
End With
intRecordIndex = intRecordIndex + 1
Next
End Sub
Download the VB project code for the example above here.